INSOLVENCY DURING COVID-19 PERIOD
The French Parliament has by virtue of an emergency law dated 23 March 2020 empowered the French Government to take all necessary measures in order to cope with the economic, financial and social consequences of Covid-19 spread.
The Government enacted a first batch of 25 ordinances, two of which directly impact the French legal insolvency regime.
The ordinance n° 2020-306 dated 25 March 2020 related to suspension of time lapsing during the health emergency period dealing mainly with administrative and judicial time periods but also certain contractual delays and impacting pending payments suspension filing as well as creditors’ statement of claims filing.
The ordinance n° 2020-341 dated 27 March 2020 worth adaptations to insolvency rules aiming in particular at:
- the suspension of insolvency filing obligation binding on companies and their managers;
- preserving the availability of pre-insolvency proceedings even if the company becomes insolvent; and
- facilitating the formalities for filing for insolvency or for a statement of claims.
The designated purpose of such reforms consists in avoiding bankruptcies while allowing companies with difficulties to face the crisis with available tools.
- 1.1 Principe of crystallisation of the insolvency test as at 12 March 2020
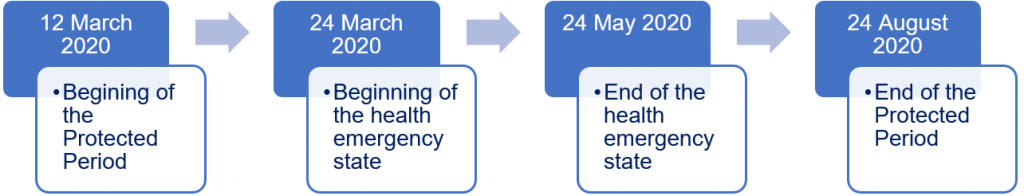
Pursuant to article I-1° of the 27 March 2020 ordinance, if, as at 12 March 2020, a company does not meet the insolvency test, it may benefit from a period of leniency.
Such a leniency period extends from 12 March (included) to 24 August 2020 (currently), which date corresponds to the expiry of the health emergency period (pending until 23 May) increased by 3 months (the ”Protected Period”).
During the Protected Period, the company may, even if it becomes insolvent:
- Continue its business in the ordinary course; or
- Petition for preventive restructuring measures (ad hoc mandate, conciliation, safegard).
As a consequence, its manager(s) may not expose their liability for late insolvency filing.
At the expiry of the Protected Period:
- if the company is no longer insolvent, which means that the Protected Period will have enabled to recover, it will then be able to continue its business;
- if the company is insolvent but for less than 45 days: it should be able to petition for the conciliation preventive proceeding measures; or if the company is still insolvent: it shall declare such an insolvency within 45 days[1].
- 1.2 – Exceptions to the insolvency test freezing as at 12 March 2020
Article I-1° of the 27 March 2020 ordinance expressly provides for exceptions to the insolvency test freezing as at 12 March 2020, as follows:
- Those pertaining to the insolvent company: maintaining during the Protected Period of the option to request the opening of bankruptcy proceedings (administrative receivership – redressement judiciaire – or judicial winding-up): such option though is only open to the benefit of insolvent companies, to the exclusion of their creditors.
- Those pertaining to courts: a judicial carry back of the payments suspension date is possible under the following scenarios:
-
- Hardening period by the application of the provisions of indents 2°, 3° and 4° of article L. 631-8 of the French commercial code: the court may carry back the payments suspension date to a date prior to the judgement opening the bankruptcy proceedings. Thus, the payments suspension date could be carried back to a date that would be prior to 12 March 2020, i.e. the beginning of the Protected Period.
-
- Incase of fraud, possibility to fix a date of payments suspension that is posterior: this exception is not crystal clear but it could be construed, in our view, as allowing the judge to postpone, in case of fraud and in the instance of a later insolvency filing beyond the 12 March 2020, to fix the payments suspension date during the Protected Period, it being at a date which is posterior to the 12 March.
The ordinances dated 25 March and 27 March 2020 provide for some guidelines as regards the time limits and obligations applicable to companies which were insolvent for less than 45 days as at 12 March 2020. However, in the absence of specific provisions relating to this specific case, the following options could be considered:
- Option a): based on the ordinance dated 27 March 2020, a company which was in a state of payments suspension for less than 45 days as at 12 March 2020 should be entitled to benefit from conciliation proceedings (procedures de conciliation) during the Protected Period although it would become in a state of suspension of payments for more than 45 days during this period of time[2];
- Option b) : based on the ordinance dated 25 March 2020, these companies should officially file for bankruptcy at the latest within 45 days as from the end of the health emergency period increased by one month (i.e. within 45 days as from 24 June 2020)[3].
A clarification from the French Government as regards the relationship between these two options would prove useful.
[2] Based on a ministerial circular dated March 30, 2020 relating to the ordinance dated 27 March 2020, it is indeed specified that the calculation of the duration of the state of suspension of payments for the purposes of opening of a conciliation proceedings should not take into account the period elapsed after the 12 March.
[3] Indeed, based on the ordinance dated 25 March 2020, the time limit for the filing of the declaration should be suspended. In addition, one interpretation of the circular dated 26 March explaining certain items of the ordinance, would lead to consider that the suspension is worth interruption and that the time limit for the filing of the declaration should run again, in full, from 24 June until 20 August 2020.
- Impossibility to file for insolvency of the debtor: generally, the bankruptcy proceedings can also be initiated by creditors. However, creditors are prevented from doing so during the Protected Period.
- Arrangements for filing declarations of claims:
-
- The ordinance dated 25 March 2020 applies to the declaration of claims. As a consequence, the filing, if it should take place within a period expiring between 12 March and 24 June 2020 (that is to say at the expiry of the health emergency period increased by one month), may be made until the expiry of a new period of two months running from 24 June.
Indeed, the suspension of the time limits has been provided for a shorter duration than the Protected Period, the latter being applicable for the insolvency test but also for the possible adaptations of the time limits relating to ongoing proceedings.
-
- As it stands, it seems that the ordinances have not considered the claims that should be filed by foreign companies, which are normally granted with a four-month period to file their claims. Therefore, to be on the safe side, it would be recommended to file the declaration of claims at the latest within two months as from 24 August.





Sanctions Against Russia. Recent Developments
On 23 February 2024 European Union and the United States introduced a new round of sanctions targeting Russia. The 13th package of European sanctions provides for new individual sanctions, sectoral sanctions, export restrictions. Additionally, EU added the United Kingdom to the list of partner countries for the iron and steel import restrictions. American sanctions include […]
Moscow Desk
Newsflash – Corporate – Venture Capital – French government announcements to support Innovative Startup Companies (JEI)
For the occasion of the French Tech’s 10th anniversary, new measures stemming from the report of Parliament Member Paul Midy (for which Jeantet had been consulted) have been announced. These measures, which aim at supporting the French startup ecosystem, should be included in the next Finance Act for 2024. ► Doubling of companies eligible to […]
| CORPORATE – M&A – PRIVATE EQUITY
Russian Counter Measures. Recent Developments
On 23 August, the Russian Ministry of Finance partially lifted a ban for the payment of dividends to foreign shareholders in case such shareholders have invested in the Russian economy. On 8 August, the Russian President suspended certain provisions of double tax treaties. Suspended provisions include tax regime for dividends, real estate, business profit, etc […]
Moscow Desk
Sanctions Against Russia. Recent Developments
On 23 June 2023, the EU introduced 11th package of sanctions. It primarily focuses on measures that would prevent circumvention of sanctions. It also includes new import and export restrictions and individual designations. Switzerland has joined European Union in sanctions targeting entities and individuals and may join other sanctions within the 11th package in August. […]
Moscow Desk
Newsletter – Tax law
Read the Jeantet Newsletter dedicated to Tax Law, covering issues related to : Transactional taxation Group taxation International Taxation Taxation of LBO transactions Non-profit organizations For more information, please download the Newsletter.
Paris | TAX
Russian Counter Measures
On 25 April 2023 Russian President issued a decree establishing cases authorizing him to introduce the regime of external management of certain assets owned by foreign residents. Namely, under the decree, the President may establish the regime of external management, if Russia, or its entities and individuals become deprived or risk of being deprived of […]
Moscow Desk
Russian counter measures and measures aimed at business support. Recent developments
Special regime for transactions involving securities On 3 March 2023 Russian President issued Decree No. 138 establishing additional measures involving securities. Namely, the new Decree establishes a specific procedure for transactions / operations involving: shares of Russian joint-stock companies, sovereign bonds, bonds of a Russian issuer, held in collective safe custody of a Russian depository, […]
Moscow Desk
Sanctions against Russia. Recent developments (2 march 2023 update)
By the end of February, the EU, US and UK announced new rounds of sanctions, all of them including restrictions targeting prominent Russian financial institutions The EU package includes individual listings of Russian entities and individuals and additional exports restrictions. The US sanctions provide for sectoral sanctions targeting Russian mining and metals sector, as well […]
Moscow Desk
Russian counter measures. Recent developments ( 12 january 2023 update)
Governmental Commission on Foreign Investments revised rules on the sale of assets and the payment of dividends On 30 December 2022, Russian Governmental Subcommission of the Commission of the Ministry of Finance on Foreign Investments (the – Commission) published revised rules and criteria for authorization of the sale of assets in Russian companies involving persons […]
Moscow Desk
Sanctions against Russia. Recent Developments (21 December 2022 update)
This December, the EU introduced a series of restrictive measures targeting Russia. Council of the EU approved the ninth package of sanctions. Additionally, the European Commission proposed framework that would amend the Lisbon Treaty and harmonize criminalization of violation of sanctions at the level of the Union. Finally, the EU introduced a price cap for […]
Moscow Desk
Russian counter measures. Recent developments (21 December 2022 update)
Russia has adopted a series of new measures. Namely, the President introduced new restrictions concerning certain transactions involving credit organizations and joint-stock companies that are not credit organizations. The Russian Central Bank issued decision expanding the scope of application of type C accounts. Moreover, the Ministry of Finance issued clarifications on the scope of transactions […]
Moscow Desk
Legal Alert: The submission to derogation of protected species: the Council of State finally pronounces itself
In an opinion n°463563 issued on December 9, 2022, the Conseil d’Etat finally provided an answer to the questions raised by the Administrative Court of Appeal of Douai in its decision n°20DA01392 of April 27, 2022 >> download the article
Paris | ENERGY AND NATURAL RESOURCES LAW | PUBLIC LAW – PUBLIC CONTRACTS | ENVIRONMENT